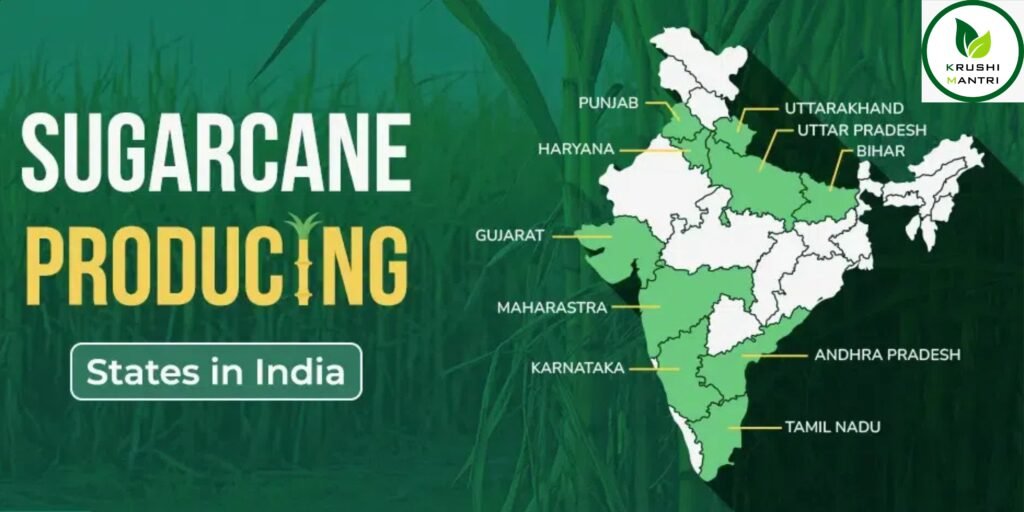
India is the second-largest producer of sugarcane globally, with Maharashtra being one of the leading states in its cultivation. Sugarcane farming is vital to the agricultural and economic landscape of India, contributing significantly to sugar, jaggery, ethanol, and other by-products. Maharashtra, with its fertile soil and favorable climate, plays a crucial role in sugarcane production, making it a hub for sugar mills and associated industries.
This guide explores sugarcane farming practices, production techniques, harvesting methods, and marketing strategies, with a special focus on India and Maharashtra.
Significance of Sugarcane Farming in India and Maharashtra
- National Contribution:
- India accounts for nearly 20% of global sugarcane production.
- Sugarcane supports industries like sugar mills, ethanol production, and jaggery-making.
- Role of Maharashtra:
- Maharashtra is the second-largest sugarcane-producing state in India after Uttar Pradesh.
- Known for its organized cooperative sugar factories, the state is a pioneer in modern sugarcane farming.
- Economic Impact:
- Provides livelihoods to millions of farmers and workers.
- Contributes to biofuel production under the Ethanol Blending Program (EBP).
Key Sugarcane Production Insights
- Climate and Soil Requirements:
- Ideal temperature: 21°C to 27°C.
- Rainfall: 750–1200 mm annually.
- Suitable soils: Deep, well-drained loamy soils rich in organic matter.
- Varieties of Sugarcane in India:
- CO 0238: Popular in Maharashtra for high sugar recovery.
- BO 147: Grown in northern India.
- CO 86032: Suitable for tropical regions.
- Planting Seasons:
- Autumn Planting: September to October.
- Spring Planting: February to March.
- Adsali Planting: July to August (common in Maharashtra).
- Intercropping:
- Farmers often grow pulses, onions, or vegetables alongside sugarcane to maximize profits.
Sugarcane Production Practices
- Land Preparation:
- Deep plowing and leveling are essential.
- Use of organic manure and green manuring improves soil fertility.
- Planting Methods:
- Ridge and Furrow Method: Ensures proper drainage and aeration.
- Trench Planting: Improves water and nutrient uptake.
- Irrigation Management:
- Requires regular watering, especially during critical growth stages.
- Maharashtra farmers adopt drip irrigation to conserve water.
- Fertilizer Application:
- Apply nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium at recommended doses.
- Use bio-fertilizers for sustainable farming.
Sugarcane Harvesting
- Optimal Harvest Time:
- Sugarcane is ready for harvest in 10–18 months, depending on the variety.
- Ensure maximum sugar content by harvesting at peak maturity.
- Manual vs. Mechanical Harvesting:
- Manual: Common in India, using labor to cut stalks.
- Mechanical: Gaining popularity in Maharashtra, reducing labor dependency and time.
- Post-Harvest Practices:
- Transport the harvested cane to sugar mills immediately to prevent sucrose loss.
Marketing Strategies for Sugarcane
Effective sugarcane marketing involves collaborating with cooperative sugar mills, producing value-added products like jaggery and ethanol, and exploring export opportunities. By leveraging government support and market trends, farmers can maximize profits.
- Selling to Sugar Mills:
- Maharashtra has numerous cooperative and private sugar mills that directly procure sugarcane from farmers.
- Farmers’ cooperatives often negotiate better prices.
- Producing Value-Added Products:
- Jaggery and jaggery powder are high-demand products in both domestic and export markets.
- Ethanol production is a growing market under government initiatives like the Ethanol Blending Program.
- Export Opportunities:
- India exports sugar and jaggery to countries in Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
- Maharashtra-based companies lead in exporting high-quality sugar.
- Government Support:
- Schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY) assist with irrigation for sugarcane farmers.
- Subsidies are available for drip irrigation and mechanical harvesters.
Organic Sugarcane Farming: A Sustainable Approach
Organic sugarcane farming focuses on growing sugarcane without synthetic chemicals or fertilizers, using natural alternatives to improve soil health and crop yield.
Benefits of Organic Sugarcane Farming:
- Premium Market Value: Organic sugar and jaggery fetch higher prices in domestic and international markets.
- Eco-Friendly: Promotes biodiversity and reduces environmental impact.
- Healthier Soil: Organic methods improve soil fertility and structure over time.
Practices in Organic Sugarcane Farming:
- Use of compost, vermicompost, and green manures for soil nutrition.
- Adopting crop rotation and intercropping with legumes to maintain soil balance.
- Relying on bio-pesticides and natural pest control methods like neem-based sprays.
Market Potential:
With rising consumer demand for organic products, organic sugarcane farming opens doors to niche markets and export opportunities. Farmers can also benefit from certifications like India Organic and USDA Organic to boost credibility.
Challenges in Sugarcane Farming
- Water Scarcity:
- Sugarcane is a water-intensive crop, and Maharashtra often faces drought conditions.
- Drip irrigation is essential to address this issue.
- Pests and Diseases:
- Common problems include red rot and top shoot borer.
- Use resistant varieties and integrated pest management (IPM) practices.
- Price Fluctuations:
- Farmers are vulnerable to changing sugar prices in domestic and international markets.
- Delayed Payments:
- Farmers often face delays in payments from sugar mills, impacting their cash flow.
Future of Sugarcane Farming in Maharashtra
With advancements in irrigation technology, government support for ethanol production, and the adoption of high-yielding varieties, sugarcane farming in Maharashtra is poised for growth. Farmers can maximize profitability by integrating sustainable practices, diversifying into value-added products, and adopting modern machinery for efficient harvesting.
Conclusion
Sugarcane farming is the backbone of India’s sugar industry and a vital part of Maharashtra’s agricultural economy. By focusing on efficient production techniques, timely harvesting, and strategic marketing, farmers can enhance their incomes while ensuring sustainable farming practices.
With its rich potential and evolving opportunities, sugarcane farming continues to be a promising venture for Indian farmers.
- Nano Urea & Nano DAP Complete Guide for Indian Farmers 2026 – Price, Benefits, Dosage, Disadvantages & Honest Review

- Bharat VISTAAR 2026: Complete Guide to AI Tool for Farmers – Helpline, Features, Schemes & How to Use

- Goat and Sheep Farming Business in India 2026 – Subsidy, Loan, Profit & Complete Guide

- Bharat VISTAAR Launch 2026: AI Tool for Farmers Goes Live Today – Weather, Prices, Pests & Schemes in Your Language – How to Use!

- India-US Trade Deal 2026: Soyabean Prices Crash 10%, Nationwide Protests Erupt – Full Details, Impacts & FAQ for Farmers

- How to Correct Your Farmer ID Online: A Step-by-Step Guide for Indian Farmers

















1 thought on “Unlocking the Potential of Sugarcane Production in Maharashtra: Expert Tips for Farming, Harvesting, and Marketing”