The Green Gold Rush: Pistachios in India
Greetings, fellow farmers and agriculture enthusiasts! I am Krushimantri, and I am excited to share my personal experience and knowledge about pistachio cultivation in India with you. As you may know, pistachio cultivation is rapidly gaining popularity in India, and the country is now making its mark in the global pistachio market. With its diverse range of climates, India has several regions that are ideal for growing pistachios. Given the right conditions, pistachio trees can grow and flourish, yielding high-quality nuts that are not only delicious but also nutritious. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of pistachio cultivation in India, including the best practices for cultivation and harvesting, as well as the history and significance of this growing industry. So, sit back, relax, and let’s explore the world of pistachios together!
How Increased Pistachio Production Supports Indian Farmers
Now, you might be wondering: aside from satisfying our snack cravings, how does growing more pistachios here at home truly benefit the people who cultivate them? Let’s crack this nut wide open!
First and foremost, boosting local pistachio production means farmers have an exciting new profit avenue. As demand for dry fruits soars across India, pistachio growers can fetch better market rates—especially for high-quality, organically grown harvests. This shift not only promises a premium for their hard work but could gradually reduce dependence on costly imports.
Choosing organic methods also comes with added perks:
- Sustainability: Organic farming helps maintain healthy soil and protects our environment for generations to come.
- Better Market Access: With export potential on the rise, Indian pistachios could find their way from Rajasthan fields to tables in Europe and the Middle East.
- Improved Rural Livelihoods: More farmers entering pistachio cultivation translates to job creation and economic upliftment in rural communities.
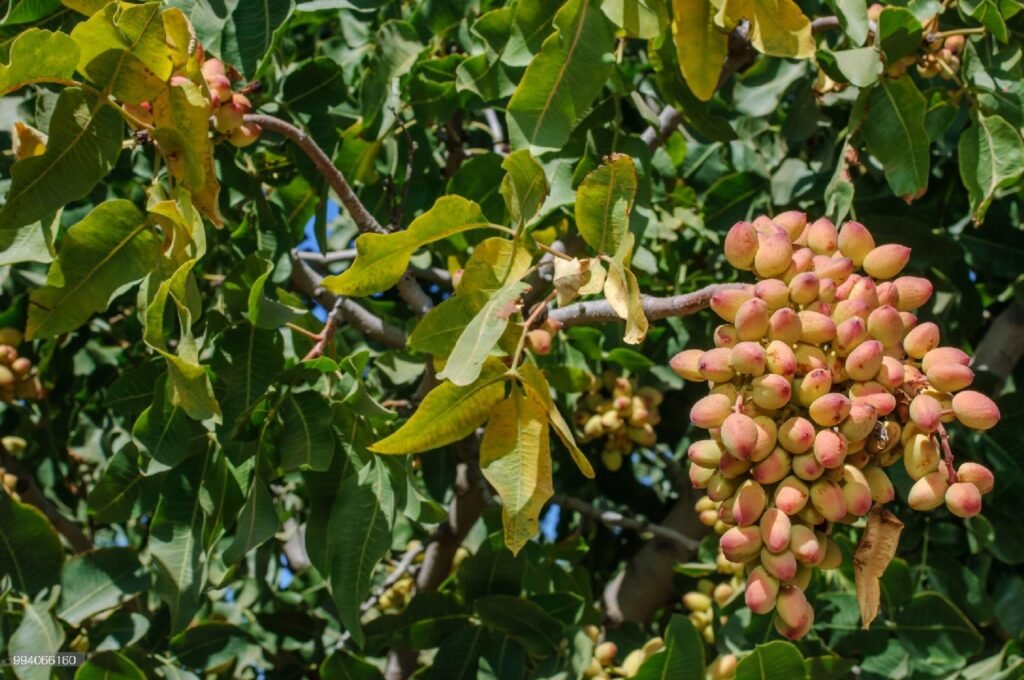

By exploring and investing in this vibrant “green gold,” Indian farmers have the chance to harvest not just nutritious nuts but a brighter, more sustainable future for themselves and their families. And if you ask me, that’s a reward worth celebrating!
Primary Uses and Market Demand for Pistachios in India
Now, you may be wondering—what exactly are pistachios prized for here in India? Well, their popularity has soared across a variety of uses. Pistachios are a favorite ingredient not only in traditional Indian sweets like kulfi, baklava, and barfi, but also as a crunchy addition to festive desserts and rich gravies. Many health-conscious folks enjoy them as a quick, energizing snack, thanks to their great taste and impressive nutritional profile.
Beyond the kitchen, pistachios are in growing demand at bakeries and confectioneries, and are often featured in premium gift boxes during festivals like Diwali and Raksha Bandhan. The rising interest in healthy eating habits has also contributed to pistachios gaining a loyal following among fitness enthusiasts, who reach for them as a protein-packed, heart-healthy option. All in all, their versatility and taste have ensured that pistachios are now an in-demand commodity on both store shelves and dining tables across the country.
India’s Pistachio Demand and Imports
At present, India’s pistachio journey is just beginning to gather pace. While our orchards are expanding every year, the majority of pistachios found on store shelves and in mithai shops still come from overseas. In fact, nearly 90% of the pistachios consumed in India are imported from established producers like Iran, the United States (particularly California), and Turkey.
That being said, there is rising excitement around domestic cultivation; experimental plantations in Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Rajasthan are beginning to bear fruit. If these efforts continue and succeed, we may soon see more homegrown pistachios on our plates and less reliance on imports.
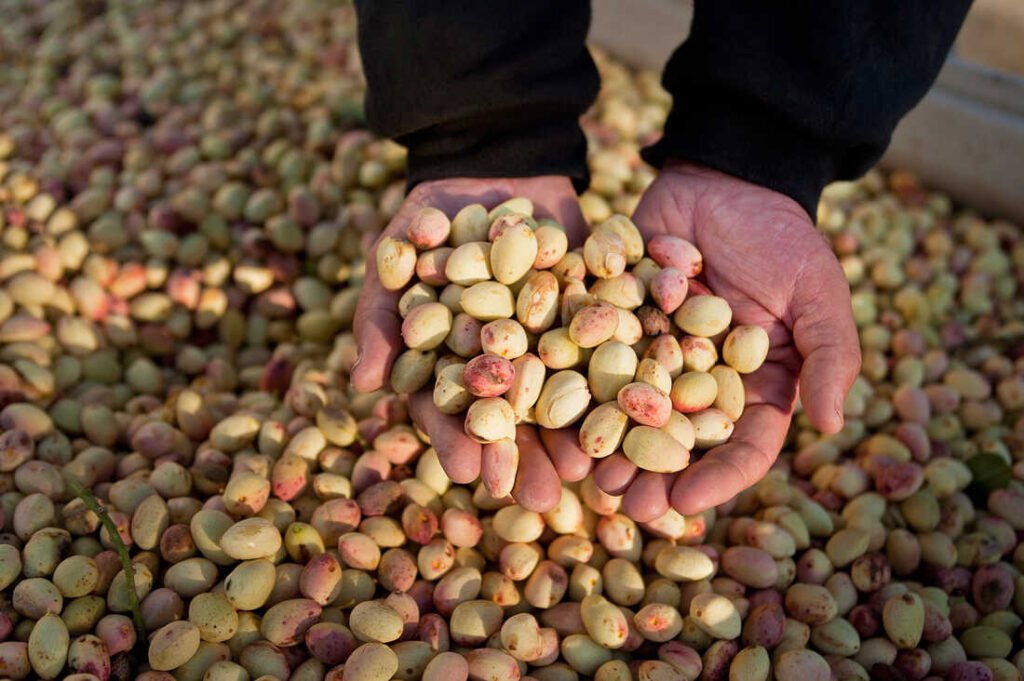

Types of Pistachio in India
Kerman:-
- Characteristics
- Kerman pistachios are known for their large size and elongated shape.
- They have a thin, light-colored shell that is easy to crack.
- The nuts themselves are light green in color and have a slightly sweet flavor.
- Production in India
- Kerman pistachios are one of the most popular types of pistachios grown in India.
- They are mainly cultivated in the states of Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
- In recent years, there has been an increase in the cultivation of Kerman pistachios due to their high demand in both domestic and international markets.
- India’s Kerman pistachio production has been steadily increasing, with estimates of up to 10,000 metric tons of production annually.
While India’s pistachio production is still in its early stages compared to leading global producers, Kerman varieties are paving the way for a promising future. Nearly 90% of India’s pistachio consumption is met through imports, but pilot projects in states like Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Rajasthan show encouraging results. With domestic demand on the rise and support from government and agricultural research institutes, more farmers are considering pistachio cultivation especially organic methods—as a viable crop. This shift could steadily reduce India’s dependence on imports and open up new opportunities for Indian farmers.
Sirora:-
- Characteristics
- Sirora pistachios are a local variety found in the Jammu and Kashmir region of India.
- The nuts are small in size and have a thick shell.
- They are known for their rich flavor and are often considered to be one of the best-tasting varieties of pistachios.
- Production in India
- Sirora pistachios are primarily grown in the Jammu and Kashmir region of India.
- The trees are typically grown in rocky, hilly terrain and require a cold, dry climate to thrive.
- The nuts are harvested in the late summer months and are often sold both in-shell and shelled.
- While Sirora pistachios are not as widely produced as some other varieties, they are still a popular choice among consumers who appreciate their unique flavor and texture.
Peshawari:-
- Characteristics
- Peshawari pistachios are small to medium-sized nuts with a slightly darker shell than other varieties.
- The nuts have a unique flavor that is described as slightly sweet and nutty, with a slightly firmer texture than other types of pistachios.
- Peshawari pistachios are also known for their nutritional benefits, as they are high in protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals.
- Production in India
- Peshawari pistachios are not native to India, but are grown in the Peshawar region of Pakistan, which is adjacent to India.
- In India, Peshawari pistachios are primarily grown in the Jammu and Kashmir region, where they are a popular local crop.
- The production of Peshawari pistachios in India is relatively small compared to other varieties, but they are still a valued and sought-after product among consumers who appreciate their unique flavor and texture.
Kale Ghuchi:-
- Characteristics
- Kale Ghuchi pistachios are a local variety grown in the Bikaner district of Rajasthan, India.
- They are small in size and have a thick, dark shell.
- The nuts have a unique flavor profile that is rich and nutty, with a slightly sweet aftertaste.
- Kale Ghuchi pistachios are also known for their high oil content, which makes them ideal for use in cooking and baking.
- Production in India
- The Bikaner district is the main region for Kale Ghuchi pistachio cultivation in India.
- The arid climate and soil conditions in this region are ideal for growing this variety of pistachios.
- Kale Ghuchi pistachios are primarily grown by small farmers who rely on this crop for their livelihoods.
- While the production volume of Kale Ghuchi pistachios is relatively small compared to other varieties, they are still highly prized by consumers who appreciate their unique flavor and quality.
Red Aleppo:-
- Characteristics
- Red Aleppo pistachios are known for their unique reddish hue and distinct flavor.
- The nuts have a slightly softer texture than other varieties, making them popular for use in desserts and pastries.
- Production in India
- While Red Aleppo pistachios are not as commonly grown in India as other varieties, they can still be found in some regions.
- Iran is the largest producer of Red Aleppo pistachios, but some Indian farmers have started cultivating the variety due to increasing demand from consumers who appreciate its unique flavor and appearance.
Pista Cultivation in India – A Growing Opportunity
The pistachio, or pista, is commercially cultivated in several countries including Iran, the USA, Turkey, and Syria—nations that dominate the global market. In India, however, the crop is still finding its footing. Pilot projects and small-scale cultivation are emerging in states such as Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, and parts of Karnataka and Maharashtra. These regions, with their suitable climates, are showing promise, especially for organic cultivation practices.
Currently, domestic production remains limited, with nearly 90% of India’s pistachio requirements being met through imports. However, increased awareness and support from agricultural research institutes and government initiatives are encouraging more Indian farmers to explore pistachio cultivation. If this trend continues and more organic practices are adopted, India has the potential to reduce its reliance on imports and offer new opportunities for local farmers—especially with specialty varieties like Red Aleppo gaining popularity among consumers.
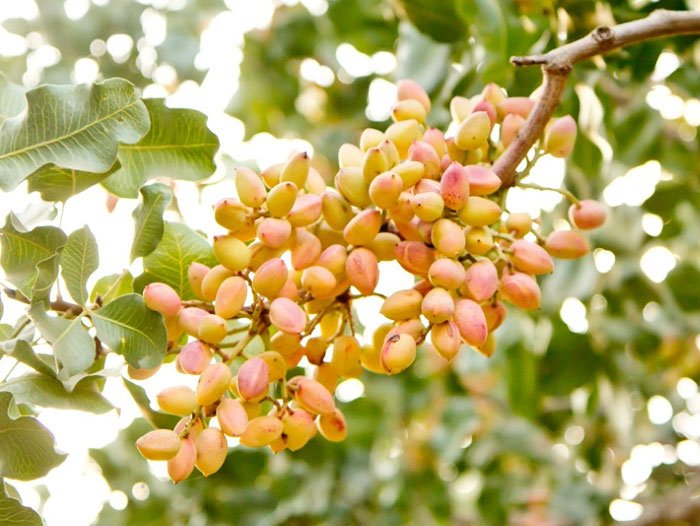
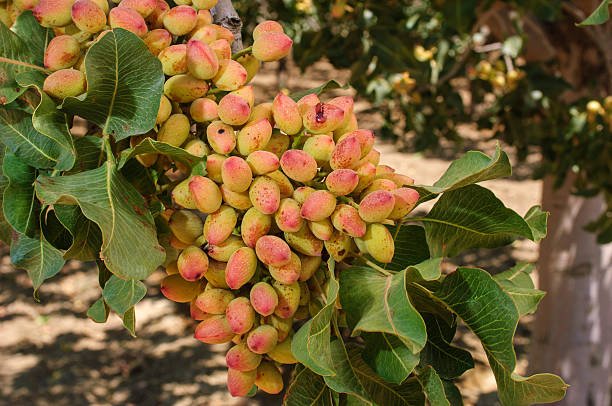


Read:- Maharashtra Farmer Success Story (Rs. 19 Lakh)
Is Pistachio Farming Profitable in India?
Absolutely—pistachio farming holds strong profit potential for Indian growers. While patience is key, as trees take several years to mature and begin yielding well, the rewards are significant. Pistachios enjoy high demand in India’s domestic market, especially among health-conscious consumers and gourmet food producers, who are willing to pay a premium for quality, organically grown nuts.
With prices remaining robust and input costs relatively stable, more Indian farmers are exploring pistachio cultivation as a promising long-term investment. The crop’s limited supply—compared to imported varieties from places like Iran or California—can also give Indian-grown pistachios an edge in local markets. For growers willing to wait for trees to reach maturity, the financial payoff can be substantial.
Requirements for Pistachio Cultivation in terms of Technical
Initial Investments for Pistachio Farming
Starting a pistachio farm requires a significant upfront investment. Some of the major initial costs include:
- Grafted Seedlings: Quality grafted pistachio saplings can be quite expensive, but they are essential for ensuring good yields and disease resistance.
- Drip Irrigation System: Setting up a reliable drip irrigation system is crucial, especially in the arid and semi-arid zones where pistachios are typically grown. This helps maintain the necessary soil moisture while conserving water.
- Land Preparation: Preparing the land—leveling, plowing, and adding required soil amendments—can also add to your costs.
- Fencing and Infrastructure: Protecting young plants from grazing animals and setting up basic infrastructure like storage or small sheds is important in the early stages.
Careful planning and an understanding of these initial costs will help set your pistachio farm up for long-term success.
Organic Pistachio Farming in India
- What is Organic Pistachio Farming?
- Organic pistachio farming involves cultivating pistachio trees without the use of synthetic chemicals or fertilizers. Instead, farmers use natural resources like compost, cow dung, neem cake, and plant-based manures to nourish their orchards. Pest and disease control relies on eco-friendly solutions such as neem oil sprays, pheromone traps, and manual weeding rather than chemical herbicides and pesticides.
- Why is Organic Farming Gaining Popularity?
- The shift toward organic pistachio cultivation in India is largely driven by growing consumer demand for healthier, residue-free foods. Health-conscious buyers—especially in urban markets—are seeking organic snacks and ingredients, fueling interest among farmers to switch to organic practices.
- Organic farming improves soil structure and fertility over time, thanks to sustainable inputs and better water management techniques like drip irrigation. This approach not only helps the environment but often fetches higher market prices for the harvest, offering greater profits for farmers.
- Key Benefits
- Enhanced soil health and biodiversity
- Reduced exposure to harmful chemicals for both farmers and the environment
- Potential for premium pricing and entry into export markets, where organic certification is valued
Farmers adopting organic pistachio farming in states like Rajasthan and Jammu & Kashmir are beginning to tap into this lucrative and sustainable market shift, meeting both local and international demand for organic nuts.
Soil:-
The soil requirements for Pistachio cultivation in India are as follows:
- Pistachio trees can grow in a variety of soil types, but they thrive best in well-drained soils with a pH level between 7.0 and 8.0.
- Soil texture should be sandy loam or loam, as pistachios do not grow well in heavy clay soils.
- The soil should be rich in nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as trace elements like zinc and iron.
- The soil should have good water holding capacity and adequate drainage to prevent waterlogging, which can damage the roots of the trees.
- The ideal depth of the soil for pistachio cultivation is between 1.5 and 2 meters.
- The soil should be free from salinity and alkalinity, which can inhibit growth and reduce yield.
However, pistachio trees are well known for their hardiness and adaptability:
- They can tolerate saline and alkaline soils better than most other fruit trees, making them ideal for semi-arid regions where other crops might struggle.
- Well-drained, sandy-loamy soils with low humidity are especially favorable, and pistachio trees are capable of surviving in soils with a degree of salinity that would be detrimental to many other crops.
- Though they are drought-tolerant, pistachios still benefit from low to moderate rainfall (30–50 cm annually), but excess water or persistent humidity can be harmful.
- The optimal temperature for pistachio growth is between 15°C and 35°C, with a maximum temperature of 40°C and a minimum temperature of -10°C.
Climate:-
The climate requirements for Pistachio cultivation in India are as follows:
- Pistachio trees require a dry and arid climate, with low humidity and plenty of sunshine.
- They are typically grown in regions that have hot summers and cold winters.
- The ideal temperature range for pistachio trees is between 15-30°C.
- Pistachios require a significant amount of chilling hours during the winter months to promote proper blooming and fruit development.
- The trees are highly drought-tolerant, but they require regular watering during the growing season.
- Soil with good drainage is essential for pistachio cultivation, as waterlogged soil can lead to root rot and other issues.
- Pistachios are often grown in areas with high soil salinity, as they are able to tolerate salt levels that other crops cannot.
To sum up:
Pistachio trees flourish in hot summers (ideally 35–40°C) and need cold winters (sometimes even below 7°C) to ensure proper bud development and fruit set. They prefer dry, arid climates and naturally do well in regions that experience low to moderate rainfall. This makes parts of Rajasthan, Punjab, and Jammu and Kashmir—where hot, dry weather and well-draining soils are common—especially suitable for pistachio cultivation. The hardy, drought-resistant nature of the pistachio tree, along with its tolerance for saline soils, allows it to thrive in many semi-arid Indian regions where few other nut crops would succeed.
Planting Material:-
Here are the planting material requirements for Pistachios cultivation in India
- Pistachios are generally propagated through grafting, which involves taking a scion from a mature pistachio tree and attaching it to a young rootstock.
- The rootstock used for grafting should be compatible with the scion and should have good resistance to soil-borne diseases.
- Some common rootstock varieties used for pistachio cultivation in India include P. atlantica, P. integerrima, and P. terebinthus.
- The scion used for grafting should be selected from a mature, high-yielding tree with good nut quality.
- Pistachios are typically planted in well-drained soil with good fertility and pH levels between 7.0 and 8.0.
- The ideal planting density for pistachios in India is around 80-100 trees per acre, with spacing between trees ranging from 20-25 feet.
- Proper irrigation is crucial for the successful growth of pistachios, and farmers should ensure that their trees receive regular watering during the growing season.
Steps for Selecting and Planting Pistachio Seedlings
Selecting and planting pistachio seedlings is a critical stage that sets the foundation for a healthy orchard and a bountiful harvest. Here’s how to approach this important task:
- Choose the Right Seedlings: Always opt for grafted seedlings from reputable nurseries. Grafted plants, especially those certified to be free of common pests and diseases, offer improved yield and quality over ungrafted ones.
- Ideal Planting Time: The best time for planting pistachio seedlings in India is typically late winter to early spring. This timing allows the young plants to establish roots before the heat of summer.
- Optimal Spacing: Maintain a distance of 6–7 meters between seedlings within the orchard. Proper spacing ensures each tree receives sufficient sunlight and airflow, which is necessary for robust growth and disease prevention.
- Male and Female Tree Ratio: Since pistachios are dioecious—meaning male and female flowers grow on separate trees—plan to plant one male tree for every 8 to 10 female trees. This ratio promotes effective pollination and maximizes nut production.
- Organic Inputs for Healthy Growth: Incorporate organic materials like well-rotted farmyard manure and bio-fertilisers at the time of planting. Natural pest repellents are preferred over chemical inputs, supporting both plant health and environmental sustainability.
- Watering After Planting: Once planted, water the seedlings thoroughly. Ensure ongoing regular irrigation, especially during the initial establishment phase, while avoiding waterlogging.
By carefully selecting quality planting material and following these guidelines, farmers give their pistachio orchards the best possible start.
Importance of Male and Female Trees
Pistachio trees have a unique biology: they are dioecious, meaning individual trees produce either male or female flowers, but not both. This matters because only the female trees yield the nuts we eat, but without male trees to provide pollen, those female trees won’t produce a harvest. To ensure successful pollination—and ultimately, a healthy crop farmers should plant at least one male tree for every eight to ten female trees. This careful ratio helps maximize the chances of wind-borne pollen reaching the female flowers during the crucial blooming period. So, while you may be tempted to fill your orchard with just female trees for nuts, don’t forget their male counterparts are essential partners in the pistachio-producing process!
Preparation of Lands:-
The preparation of lands requirements for Pistachios cultivation in India includes the following:
- Soil analysis is essential to determine the suitability of the land for pistachio cultivation. The soil should have good drainage and a pH level between 7.0 to 7.8.
- Pistachio trees require a lot of sunlight and warm temperatures, so the land should be in an open, sunny location with good air circulation.
- The land needs to be prepared by removing all weeds, stones, and other debris. The soil should be tilled and leveled to a depth of at least 30 cm.
- A proper irrigation system needs to be established to ensure that the pistachio trees receive enough water. Drip irrigation is the most effective method for pistachio cultivation.
- The land should be fertilized with organic and inorganic fertilizers to provide the necessary nutrients to the pistachio trees.
- The pistachio trees should be planted at a distance of 6-8 meters between each tree to ensure proper growth and development.
- Before planting the pistachio trees, a raised bed should be created to prevent waterlogging and ensure proper drainage. This also helps in maintaining soil temperature and moisture.
Planting Pistachio Trees: Steps for Successful (and Organic) Establishment
Planting pistachio trees, whether conventional or organic, requires careful planning and a methodical approach. By following these steps, you can lay the foundation for a robust, productive orchard.
Selecting Planting Material:
Begin with healthy, grafted saplings of reliable pistachio varieties. Grafted seedlings tend to produce higher yields and are less susceptible to common soil-borne diseases. Make sure to include both male and female trees in your planting plan, since pistachios are dioecious—generally, one male for every 8–10 female trees ensures adequate pollination.
Timing and Spacing:
The best time for planting is during the winter months—from December to February—when the trees are dormant and can establish roots without weather stress. Dig planting pits about a meter deep and wide enough to comfortably accommodate the root ball. Maintain at least 6–7 meters of space between each tree. This spacing allows for sufficient sunlight, air movement, and eventual canopy growth.
Steps for Organic Cultivation:
For those steering clear of chemicals, adopt these organic practices:
- Nutrient Management: Enrich the soil with well-rotted farmyard manure, compost, green manure, or neem cake to boost fertility.
- Pest and Disease Control: Employ natural pest deterrents like neem oil sprays, Trichoderma preparations, or pheromone traps to manage pest populations without synthetic chemicals.
- Weed Management: Control weeds using mulches made from crop residues, or remove weeds manually. Avoid using herbicides.
- Watering: Install a drip irrigation system to deliver water directly to the roots, conserving moisture and reducing the risk of waterlogging.
By combining careful variety selection, correct planting techniques, and a commitment to organic inputs, growers can establish healthy, resilient pistachio orchards that meet both yield and sustainability goals.
Best Practices for Organic Pistachio Cultivation
For those aiming to produce pistachios organically, careful planning and sustainable management are key. Organic pistachio farming emphasizes maintaining soil health, reducing dependence on chemicals, and adhering to natural growing cycles. Here are some proven best practices:
- Soil Fertility: Enrich the soil by incorporating well-rotted compost, farmyard manure, and green manure crops such as dhaincha or sunn hemp. Incorporating organic matter not only boosts fertility but also improves soil structure and moisture retention.
- Natural Pest Control: Manage common pests using biological solutions like neem oil sprays, Bacillus thuringiensis, and setting up pheromone traps. Introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, helps keep pest populations in check, reducing the need for synthetic pesticides.
- Weed Management: Rather than relying on herbicides, practice regular mulching using organic materials—such as straw or dried leaves—and remove weeds manually when necessary. Mulching not only suppresses weeds but also helps to conserve soil moisture.
- Efficient Watering: Adopt drip or micro-irrigation systems to deliver water directly to the plant roots. This minimizes water waste and reduces the risk of waterlogging, which is particularly important for pistachios.
- Routine Crop Monitoring: Regularly inspect orchards for pest outbreak signs, nutrient deficiencies, or disease symptoms. Prompt attention to issues helps minimize losses and supports tree health without resorting to chemical interventions.
When growers commit to these methods, not only does it encourage healthier orchards, but organically grown pistachios often command a higher price in the market—appealing to health-conscious consumers and environmentally aware buyers alike
Planting Time and Spacing:-
- Pistachio trees should be planted during the winter season, typically from December to February.
- The ideal temperature for pistachio cultivation is between 20-25 degrees Celsius.
- Pistachio trees should be planted in well-drained soil that is rich in nutrients.
- The spacing between pistachio trees should be approximately 6-7 meters to allow for proper growth and development.
- The depth of the planting hole should be around 1 meter, and it should be wide enough to accommodate the root ball of the sapling.
- It is important to plant pistachio trees in an area that receives ample sunlight and is protected from strong winds.
- Proper irrigation is essential for the growth and development of pistachio trees, and they should be watered regularly during the first few years of growth.
Gestation Period for Pistachio Trees
- Pistachio trees generally take some patience before rewarding growers with their first harvest. Under typical Indian conditions, these trees start producing nuts about 5 to 7 years after planting.
- While initial yields in the first few bearing years may be modest, pistachio trees reach their full productive potential and provide peak harvests from around the 10th year onwards.
- Consistent care—including proper fertilization, irrigation, and disease management—will help ensure healthy growth and optimal yields as trees mature.
Manures and Fertilizers per Plant:-
- Organic manures such as farmyard manure or compost can be added to the soil before planting to improve soil fertility.
- Nitrogen is the most important nutrient for pistachio trees, and it is recommended to apply 100-150 kg/ha of nitrogen per year.
- Phosphorus and potassium are also important, and 50-75 kg/ha of phosphorus and 100-150 kg/ha of potassium are recommended annually.
- Zinc is another important micronutrient for pistachio trees, and it is recommended to apply 5-10 kg/ha of zinc sulphate.
- Fertilizers should be applied in two to three doses during the growing season, with the first dose applied before flowering and subsequent doses applied at regular intervals.
- Over-fertilization should be avoided as it can lead to salt accumulation in the soil, which can harm the tree and reduce crop yield.
Irrigation:-
- Pistachio trees require a moderate amount of water, but can be sensitive to overwatering or waterlogging.
- The amount of water required depends on several factors, such as soil type, climate, and tree age.
- In general, pistachio trees require more water during the early stages of growth and less as they mature.
- Drip irrigation is the most common method used for pistachio cultivation in India, as it allows for precise control of water delivery and minimizes water loss through evaporation.
- The frequency and duration of irrigation depend on factors such as soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and tree age.
- In some regions of India, farmers also use groundwater or rainwater harvesting techniques to supplement irrigation water and reduce dependence on surface water sources.
Pruning and Training:-
- Pruning and training are important practices in pistachio cultivation that help to maintain tree health, increase yield, and improve nut quality.
- Pistachio trees are typically pruned in the winter or early spring when the trees are dormant.
- The main objectives of pruning are to remove dead or diseased wood, maintain tree structure and shape, and promote the growth of new branches.
- Pistachio trees require a strong central leader, which is achieved through the removal of competing branches and careful training of the main stem.
- Young trees should be trained to have a central leader with a clear trunk of at least 24 inches before branching out.
- As the tree grows, lateral branches should be pruned to maintain the desired shape and to prevent the tree from becoming too dense.
- Pruning should be done carefully to avoid damaging the tree, and the use of proper pruning tools is important to ensure clean cuts and minimize damage to the bark.
- Pruning should also be done with consideration for the timing and intensity of pruning, as this can affect the yield and quality of the crop in the following year.
Intercrops:-
- Pistachio trees require full sunlight, so any intercrops should be selected to avoid shading the trees.
- Intercrops should be selected based on their compatibility with pistachios, as well as their potential to improve soil quality and provide additional income for farmers.
- Leguminous crops, such as beans, peas, and lentils, are often recommended as intercrops because they help fix nitrogen in the soil and can provide additional income for farmers.
- Cover crops, such as clover, rye, and vetch, can also be planted between rows of pistachio trees to help control weeds and improve soil quality.
- Care should be taken to avoid planting intercrops that are susceptible to diseases or pests that could spread to the pistachio trees.
- Intercrops should be managed carefully to ensure they do not compete with pistachio trees for water or nutrients.
- In some cases, intercrops may need to be removed before the pistachio trees reach maturity to avoid competition and ensure a good harvest.
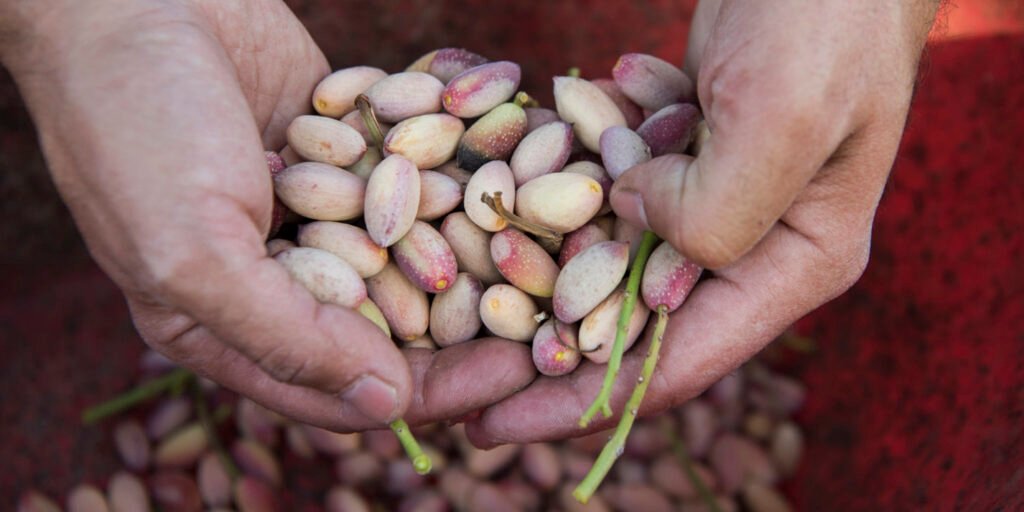
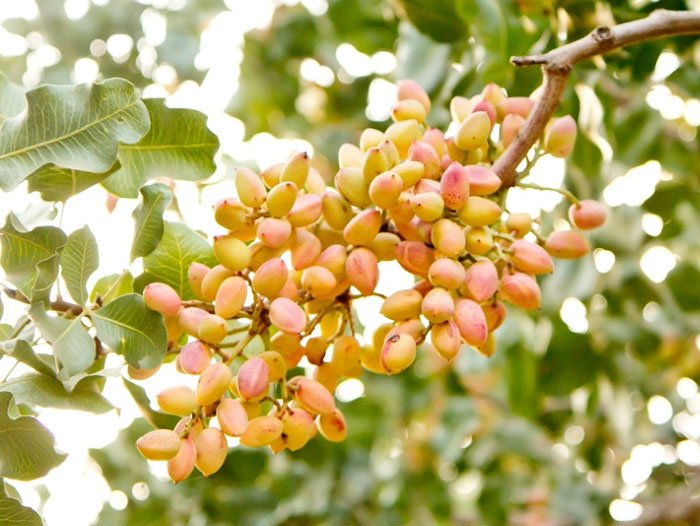



Bahar Treatment and it’s Need:-
- Bahar treatment is a process that involves exposing pistachio trees to cold temperatures to promote flowering and fruit production.
- The treatment is typically done in winter, when the temperature drops to around 0-7°C, which is ideal for the process.
- Pistachio trees require a certain number of cold hours (between 800 to 1200 hours) for successful Bahar treatment.
- The duration of Bahar treatment depends on the variety of pistachio being cultivated, with some requiring longer periods of cold exposure than others.
- In India, Bahar treatment is typically done in the northern regions, such as Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Punjab, where the climate is suitable for the process.
- Successful Bahar treatment is essential for high-quality pistachio production, as it helps to promote flowering and fruit set, resulting in a larger yield.
Controlling of Fruit Drop:-
- Water management: Pistachio trees require moderate watering during the growing season, but excessive watering can lead to fruit drop. Proper water management is essential to prevent water stress in the trees, which can cause fruit to fall prematurely.
- Nutrient management: Pistachio trees require specific nutrients at different stages of growth. Proper fertilization and soil management can help prevent nutrient deficiencies that can lead to fruit drop.
- Pest and disease management: Pests and diseases can cause significant damage to pistachio trees, leading to fruit drop. Effective pest and disease management is crucial to prevent losses.
- Thinning: Overcrowded fruit on the tree can lead to fruit drop. Thinning the fruit can help improve the quality and quantity of the remaining nuts on the tree.
- Harvest timing: Timing the harvest of pistachios is crucial to prevent fruit drop. Waiting too long to harvest can cause nuts to fall from the tree due to natural abscission.
Read:-Profitable Goat Farming: An Investment Guide to Expenses and Earnings – No.1 Project Report
Pest Control:-
Here is a table outlining some common pests and diseases that can affect pistachio trees in India, as well as some methods for pest control:
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Control Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Small, green insects that suck sap from the leaves and stems of the tree. | 1) Spray the trees with insecticides containing neem oil, pyrethrin, or other natural or synthetic chemicals. 2) Encourage the natural predators of aphids, such as ladybugs and lacewings. |
| Spider mites | Tiny, red or yellow mites that spin webs on the leaves and suck sap from the tree. | 1) Spray the trees with insecticides containing neem oil or other natural or synthetic chemicals. 2) Use a high-pressure water spray to knock the mites off the leaves. |
| Pistachio twig borer | Larvae that bore into the branches of the tree, causing damage and reducing yield. | 1) Prune off affected branches and destroy them. 2) Apply insecticides to the tree during the dormant season to kill the larvae before they can cause damage. |
| Verticillium wilt | A fungal disease that causes leaves to wilt and die back, eventually killing the tree. | 1) Plant disease-resistant varieties of pistachio trees. 2) Maintain good soil drainage and avoid overwatering. 3) Apply fungicides to the tree to control the spread of the disease. |
| Root rot | A fungal disease that attacks the roots of the tree, causing them to rot and reducing the tree’s ability to take up water and nutrients. | 1) Avoid overwatering and ensure good soil drainage. 2) Apply fungicides to the soil around the tree to control the spread of the disease. |
It’s worth noting that these are just a few examples of the many pests and diseases that can affect pistachio trees, and that the best methods for pest control will depend on the specific situation and conditions of the orchard. It’s important for farmers to stay informed about the latest research and best practices for pest control in order to ensure a healthy and productive crop.
Read:-Sweet Success: How to Make a Profit of ₹160,000 with Honey Bee Farming
Main Challenges Faced by Pistachio Farmers in India
As with any crop, pistachio cultivation in India comes with its own set of hurdles that growers need to be aware of before diving in. Here are some of the key challenges pistachio farmers commonly encounter:
- Delayed Returns: Pistachio trees take several years to mature and start producing a significant harvest. This means farmers must have both patience and the resources to manage the orchard during the initial, non-productive years.
- Climate Specificity: Pistachios thrive only under particular climatic conditions—especially well-defined periods of winter chill and warm, dry summers. Not all regions in India are suitable, and unexpected weather events can impact yields.
- Knowledge Gap: Many farmers are new to pistachio farming and may lack access to reliable information or technical guidance, making it harder to manage orchards efficiently or address emerging issues.
- Upfront Investment: Establishing a pistachio orchard requires a significant initial outlay for quality grafted seedlings, setting up proper irrigation (like drip systems), and ensuring long-term maintenance.
Overcoming these challenges often requires a combination of ongoing education, support from agricultural extension services, and adopting best practices developed through research and experience. With the right resources and a bit of perseverance, many of these barriers can be tackled, opening up promising opportunities for pistachio growers in India.
Overcoming Challenges in Pistachio Farming
So, how can farmers address the hurdles of pistachio cultivation? The key lies in a proactive approach:
- Seek hands-on training: Participating in workshops, extension programs, or field demonstrations can equip growers with the practical know-how needed to tackle common pistachio problems, whether it’s pest control, irrigation management, or pruning techniques.
- Tap into government schemes: Many agricultural departments in India periodically roll out grants, subsidies, or technical support for orchard establishment and maintenance. Keeping an eye on these opportunities can help offset initial costs and provide a safety net during tough seasons.
- Build strong market connections: Joining cooperative societies, farmer producer organizations (FPOs), or even connecting with exporters and wholesalers directly can ensure better prices and steady demand for your harvest.
By combining these strategies with ongoing learning and adopting best practices suited to your local climate and soil, pistachio cultivation becomes far more manageable. With patience and persistence, Indian farmers can make pistachio farming a truly rewarding venture.
Organic Pest and Weed Management in Pistachio Orchards
Farmers aiming for an organic approach to pest and weed control have several effective strategies at their disposal. For pest management, natural options such as neem oil sprays can deter many common pests without resorting to harsh chemicals. Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings into the orchard adds an extra layer of defense, as these natural predators help keep population numbers of harmful pests, such as aphids, in check.
In terms of weed control, mulching stands out as one of the easiest and most effective techniques. Applying a thick layer of organic mulch around the base of pistachio trees suppresses weed growth, retains soil moisture, and gradually enriches the soil as it breaks down. Regular hand weeding is another tried-and-true method, allowing for precise removal of unwanted growth without disturbing the young pistachio roots or introducing residual chemicals into the environment.
By combining these organic methods—neem oil treatments, encouraging beneficial insects, mulching, and manual weeding—farmers can maintain healthier orchards while supporting soil health and sustainability.
Government and Research Support for Pistachio Cultivation
As interest in pistachio cultivation grows across India, both government agencies and agricultural research institutions are stepping up their efforts. Through workshops, farmer training programs, and field demonstrations, these organizations are disseminating crucial knowledge about best practices for pistachio farming. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and state agricultural universities, for example, are busy publishing guides and conducting studies to help farmers adapt pistachio cultivation to various agro-climatic zones.
Additionally, several state departments of horticulture offer technical support, access to quality planting materials, and guidance on pest management. Subsidies and grants for orchard establishment may also be available depending on the region, making it more feasible for new and existing farmers to diversify into pistachio production.
Staying in touch with these organizations can provide growers with the latest updates, new disease-resistant varieties, and hands-on solutions to challenges in the field. This collective effort is steadily building a strong foundation for the future of pistachio farming in India.
Harvesting:-
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Timing | Pistachio trees are usually harvested once a year, typically between August and October. |
| Preparation | Before the harvest, the ground around the trees is cleared of any debris to make it easier to collect the nuts. |
| Harvesting | There are two main methods of harvesting pistachios in India: manual and mechanical. |
| Manual harvesting | This method involves shaking the branches of the tree to release the nuts, which are then collected by hand or using nets spread on the ground. |
| Mechanical harvesting | This method uses specialized equipment that shakes the tree to release the nuts, which are then collected using conveyor belts or suction devices. |
| Cleaning and sorting | Once the nuts have been harvested, they are typically cleaned and sorted to remove any debris, twigs, or imperfect nuts. |
| Drying | After cleaning and sorting, the nuts are spread out in a well-ventilated area to dry. This can take several days, depending on the weather and humidity levels. |
| Roasting | Many pistachios are roasted before being sold to enhance their flavor and texture. This is typically done in large ovens or roasters. |
| Packaging and storage | Once the nuts have been roasted and cooled, they are packaged in airtight containers to preserve their freshness and flavor. They can be stored for several months under the right conditions. |
Expected Yield per Mature Tree
Yield:
A fully mature pistachio tree typically produces between 10 and 20 kilograms of nuts each year, depending on factors such as tree health, growing conditions, and the specific variety cultivated.
Future Outlook for Organic Pistachio Farming in India
Looking ahead, organic pistachio farming in India holds significant promise. As more growers embrace sustainable practices, the sector is poised for steady expansion. The adoption of organic methods not only supports soil health but also creates new opportunities for rural communities and small-scale farmers.
Government initiatives encouraging organic agriculture, coupled with advances in research and techniques from organizations like ICAR and international bodies, continue to pave the way for improved productivity. With growing consumer demand for healthier and chemical-free nuts, the Indian organic pistachio market is likely to carve out a unique place both nationally and internationally.
Sustained focus on innovation, farmer training, and eco-friendly cultivation will further strengthen the future prospects of organic pistachio farming across the country.
Impact of Organic Certification on Price and Marketability
Organic certification plays an important role in enhancing both the value and appeal of pistachios in the marketplace. When farmers adopt organic cultivation practices, not only do they contribute to healthier soil, but the nuts they produce are viewed as more desirable by consumers and traders alike.
- Higher Returns: Certified organic pistachios generally command a higher price than conventionally grown ones. This premium is driven by strong demand in both Indian and international markets, where buyers often seek out organic produce for health and environmental reasons.
- Market Access: Many export markets, especially in the European Union and United States, prefer or even require organic certification, making it easier for growers to access these lucrative destinations.
- Consumer Preference: Increasing awareness about food safety and sustainability means more buyers are choosing organic, which directly boosts the marketability of organically grown pistachios.
In summary, opting for organic certification allows pistachio growers to tap into premium market segments and often results in improved profits over conventional methods.
We hope this blog is vital for you; hence more information regarding any agriculture sector, stay tuned with Krushimantri.com
A Complete Guide to Pista Farming in India: Everything You Need to Know
Pistachios in India: The Complete Guide to Cultivation and Harvesting
Where Are Pistachios Grown in India? Exploring the Best Pistachio Growing Zones










2 thoughts on “Pistachios in India: The Complete Guide to Cultivation and Harvesting”